No doubt, renewable energy has become one of the most important solutions in the global effort to reduce carbon emissions, improve energy security, and protect the planet. As we are concerned of how climate change grows, governments, businesses, and individuals increasing, a path has been discovered on how we can convert clean energy sources to power homes, industries, and transportation.
Understanding the different types of renewable energy is essential for anyone who wants to make informed decisions about sustainable power systems.
Renewable energy is energy that comes from natural sources that are constantly replenished and never run out. These sources include sunlight, wind, water, heat from the Earth, and organic materials. Unlike fossil fuels—such as coal, oil, and natural gas—renewable energy does not deplete over time and produces little to no greenhouse gases when used.
Types of Renewable Energy
This comprehensive guide explores the major forms of renewable energy—how they work, their benefits, challenges, and the role they play in shaping a low-carbon future.
1. Solar Energy

Solar energy is one of the most popular and widely used forms of renewable power. It is generated by capturing sunlight and converting it into electricity or heat.
How Solar Energy Works
Solar power is produced using two main technologies:
- Photovoltaic (PV) systems – Solar panels made of semiconductor materials convert sunlight directly into electricity.
- Solar thermal systems – Mirrors or collectors concentrate sunlight to produce heat, which can then be used for water heating or electricity generation in solar thermal power plants.
Benefits of Solar Energy
- Abundant and available virtually everywhere
- Low maintenance once installed
- Significant reduction in electricity bills
- Can be installed at multiple scales—residential, commercial, and utility
Challenges you may face with solar energy
- Energy production depends on weather and daylight.
- Initial installation costs can be high.
- Requires storage systems for consistent supply.
Despite these challenges, solar energy remains one of the fastest-growing renewable sectors globally and you can find available products that meets your needs and budgets at Sulu Expert Solutions.
2. Wind Energy

Wind energy converts the kinetic energy of moving air into electricity using wind turbines. It is a clean, efficient, and increasingly cost-competitive source of renewable power.
How Wind Energy Works
- Wind turbines capture wind using blades that rotate when air flows over them.
- The turbine’s generator converts this rotational energy into electricity.
- Wind farms can be located onshore (on land) or offshore (in the sea).
Benefits of Wind Energy
- Produces no greenhouse gases during operation
- Very low operating costs once installed
- Offshore wind farms provide high power output due to stronger, steadier winds
Challenges you may face with wind energy
- Wind patterns can be unpredictable.
- Some communities oppose turbines due to visual and noise concerns.
- Requires extensive land or sea space.
Wind energy continues to grow, especially in regions that have strong and consistent wind resources.
3. Hydropower or hydroelectric power
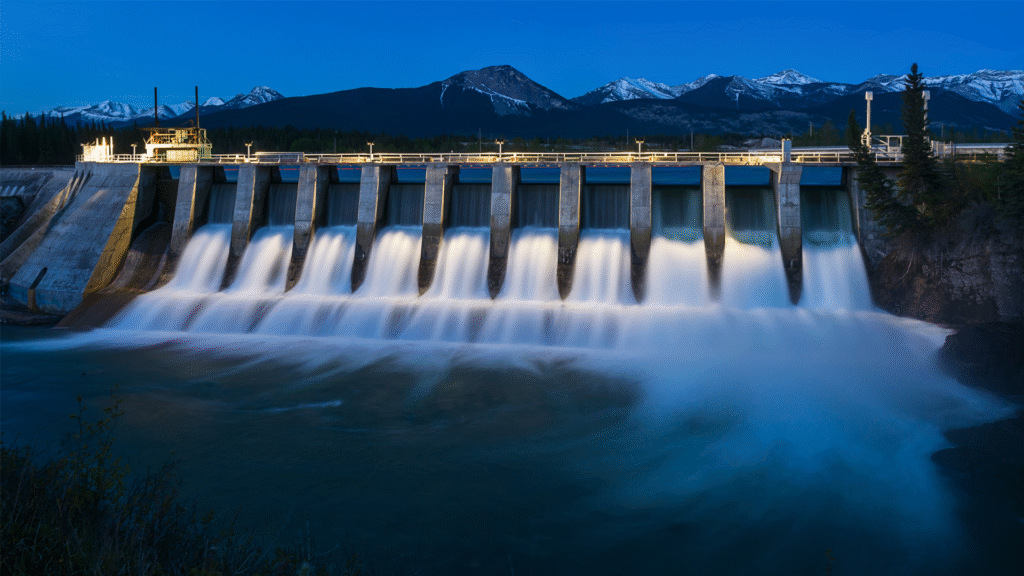
Hydropower, or hydroelectric power, is the world’s largest source of renewable electricity. It uses the movement of water to generate electricity.
How Hydropower Works
Hydroelectric systems typically use:
- Dams: Water is stored in reservoirs and released through turbines to generate electricity.
- Run-of-river systems: These use the natural flow of rivers without large reservoirs.
- Pumped storage: Water is pumped uphill during low demand and released to generate electricity during high demand.
Benefits of Hydropower
- Reliable and capable of producing large amounts of power
- Provides water management benefits like irrigation and flood control
- Long lifespan and low operational costs
Challenges you face with Hydropower
- Large dams can disrupt ecosystems and local communities.
- Vulnerable to drought and climate-related water shortages.
- High upfront construction costs.
Hydropower remains crucial for grid stability and energy storage.
4. Biomass Energy

Biomass energy is produced from organic materials, including plant matter, agricultural waste, and even household waste. It can be used to generate electricity, heat, and biofuels.
How Biomass Energy Works
Biomass can be:
- Burned directly to produce heat or electricity
- Converted into biofuels (such as ethanol or biodiesel)
- Processed into biogas through anaerobic digestion
Benefits of Biomass Energy
- Uses waste materials, reducing landfill use
- Provides a steady, controllable source of energy
- Can be carbon-neutral when sourced sustainably
Challenges you may face with Biomas Energy
- If not managed properly, biomass can contribute to deforestation.
- Produces emissions (though generally lower than fossil fuels).
- Requires careful regulation to remain sustainable.
Biomass is particularly important in regions with abundant agricultural or forestry resources.
5. Geothermal Energy

Geothermal energy harnesses heat stored beneath the Earth’s surface. This clean, reliable source of power is used for electricity generation and heating.
How Geothermal Energy Works
- Geothermal power plants pump hot water or steam from underground reservoirs to drive turbines.
- Geothermal heat pumps use the earth’s stable temperature for heating and cooling buildings.
Benefits of Geothermal Energy
- Extremely reliable—available 24/7
- Low emissions
- Highly efficient for heating and cooling
Challenges you may face with Geothermal Energy
- Limited to regions with accessible geothermal resources.
- Drilling and exploration can be expensive.
- Risk of triggering minor seismic activity in some cases.
Countries like Iceland, the U.S., and the Philippines are leaders in geothermal power.
6. Tidal Energy
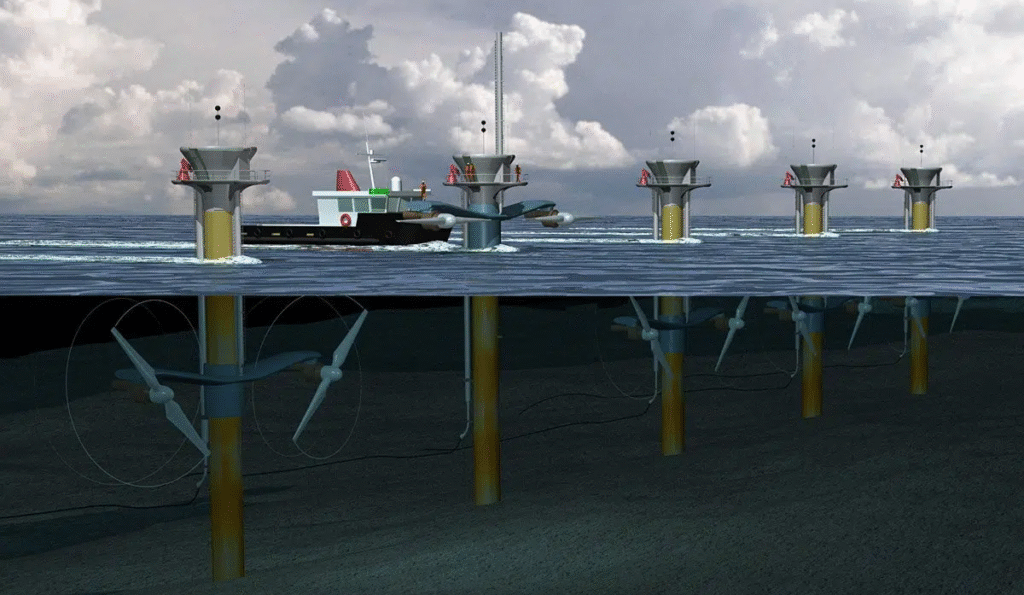
Tidal energy uses the rise and fall of ocean tides to generate electricity. Because tides are predictable, tidal power is considered one of the most reliable forms of renewable energy.
How Tidal Energy Works
There are two primary technologies:
- Tidal barrages – Large structures that capture water at high tide and release it through turbines at low tide.
- Tidal stream generators – Turbines placed underwater in fast-moving tidal currents.
Benefits of Tidal Energy
- Predictable and consistent power generation
- Very long-lasting infrastructure
- Zero emissions during operation
Challenges you may face with Tidal Energy
- High infrastructure costs.
- Potential environmental impact on marine ecosystems.
- Limited suitable locations worldwide.
Tidal energy is still emerging but shows strong potential for coastal nations.
7. Wave Energy
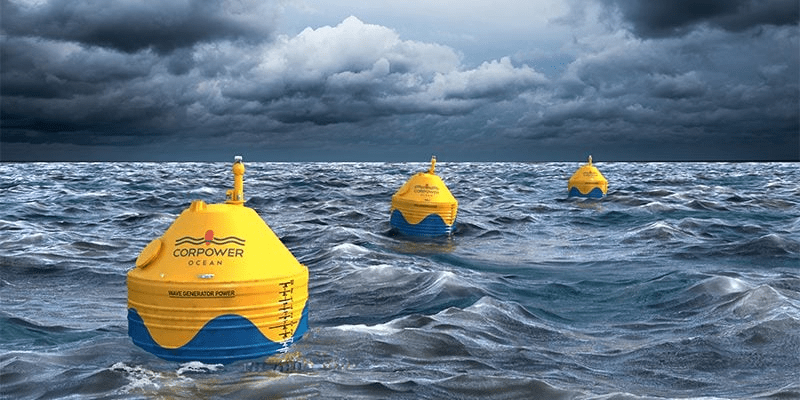
Wave energy converts the movement of ocean waves into electricity. Although still in early development, it has vast potential due to the immense power of the ocean.
How Wave Energy Works
Wave energy devices can:
- Float on the surface
- Sit on the seabed
- Capture energy through oscillating water columns
Benefits of Wave Energy
- Oceans provide a massive, untapped energy source
- Consistent power during storm seasons
- No greenhouse gas emissions
Challenges you may face with Wave Energy
- Technology is still experimental
- Harsh ocean conditions make maintenance difficult
- May impact marine life and shipping routes
Wave energy could become a significant contributor to global electricity as technology advances.
8. Hydrogen (Green Hydrogen)
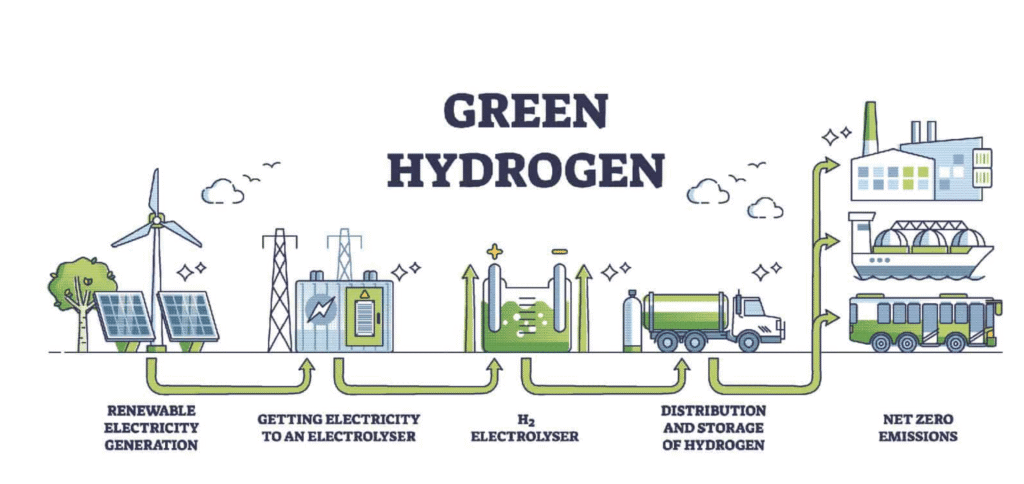
Hydrogen itself is not an energy source, but when produced using renewable energy, it becomes a powerful energy carrier. Green hydrogen is created by using electrolysis powered by renewable sources like wind or solar.
How Green Hydrogen Works
- Electricity splits water into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Hydrogen is stored and transported for use in fuel cells, industry, or transportation.
Benefits of Green Hydrogen
- Can decarbonise hard-to-electrify sectors (steel, shipping, aviation)
- Stores energy for long periods
- Produces only water vapour when used in fuel cells
Challenges you may face with Green Hydrogen
- Currently expensive to produce
- Requires large amounts of renewable electricity
- Infrastructure for transport and storage is still developing
Despite challenges, green hydrogen is seen as vital for a net-zero future.
Other Emerging Types of Renewable Energy
While the main forms dominate today’s renewable landscape, several innovative technologies are gaining attention:
1. Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC): Uses temperature differences between warm surface water and cold deep water to generate power.
2. Algae Biofuel: Produces high-energy biofuel from algae growth, potentially more efficient than traditional biomass.
3. Solar-to-Fuel Technologies: Advanced methods that convert sunlight directly into synthetic fuels.
These emerging solutions could play major roles in future energy systems.
Why Renewable Energy is Important
Renewable energy is essential for numerous environmental, economic, and social reasons;
Environmental Benefits
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions
- Decreases reliance on fossil fuels
- Protects ecosystems and biodiversity
Economic Benefits
- Creates millions of green jobs
- Reduces long-term energy costs
- Promotes energy independence for nations
Social Benefits
- Improves public health by reducing air pollution
- Expands energy access in remote areas
- Supports sustainable development
Challenges to Widespread Renewable Energy Adoption
Despite remarkable progress, renewables face hurdles:
- The need for energy storage to address intermittency.
- Limitations in existing grid infrastructure.
- The high initial cost of some technologies.
- Political and regulatory barriers.
However, ongoing innovation—especially in batteries, smart grids, and large-scale storage—is rapidly reducing these obstacles.
What is the future of renewable energy?
The future of renewable energy looks promising as technologies become more efficient and affordable. Trends shaping the future include:
- Rapid growth in solar and wind installations
- Advancements in battery technology
- Smart grid expansion
- Increased investment in hydrogen and energy storage
- Global commitments to net-zero emissions
Renewable energy is expected to dominate electricity generation in the next few decades, driving a cleaner, more resilient energy system.
In Conclusion
Understanding the types of renewable energy is key to building a cleaner and more sustainable future. From solar and wind to geothermal, biomass, and emerging technologies, renewables provide abundant, eco-friendly alternatives to fossil fuels. They help combat climate change, improve public health, and offer long-term economic benefits.
As innovation accelerates and global support increases, renewable energy will continue to revolutionise the way we power our world. Embracing these clean technologies today ensures a brighter, greener tomorrow for future generations. Shop with us today.